Wireguard
From DD-WRT Wiki
| Revision as of 00:42, 21 January 2020 (edit) Jeremywh7 (Talk | contribs) m (→Resolving local hostnames in the tunnel - typo) ← Previous diff |
Revision as of 23:37, 21 January 2020 (edit) (undo) Jeremywh7 (Talk | contribs) m (update for r42067) Next diff → |
||
| Line 29: | Line 29: | ||
| ==What is a QR Code?== | ==What is a QR Code?== | ||
| - | Since build 38581 in February 2019, a client config can be imported using | + | The "Quick Response" Code is a two-dimensional barcode with larger encoded data capacity and high fault tolerance. Since build 38581 in February 2019, a client config can be imported using a QR Code. The advantage of this approach is that there is no need to transfer sensitive information via potentially compromised data channels. |
| ==Setup Instructions== | ==Setup Instructions== | ||
| Line 43: | Line 43: | ||
| '''Create the Wireguard tunnel:'''<br> | '''Create the Wireguard tunnel:'''<br> | ||
| DD-WRT ''Basic'' -> ''Tunnels'' tab: enable the ''Tunnel'' then select ''WireGuard'' for ''Protocol Type''. | DD-WRT ''Basic'' -> ''Tunnels'' tab: enable the ''Tunnel'' then select ''WireGuard'' for ''Protocol Type''. | ||
| - | *''Generate Key'' and enter the oet1 interface IP | + | *''Generate Key'' and enter the ''oet1'' interface IP: <font color=red>must be a network outside the local LAN range</font> |
| *E.g. if the router LAN IP is 192.168.2.1, for the oet1 IP address use 10.10.0.1. | *E.g. if the router LAN IP is 192.168.2.1, for the oet1 IP address use 10.10.0.1. | ||
| Line 50: | Line 50: | ||
| '''Masquerade the tunnel:'''<br> | '''Masquerade the tunnel:'''<br> | ||
| - | Wireguard | + | Wireguard must be unbridged, using Forwarding and NAT. Go to ''Networking'', unbridge the oet1 interface (automatic since r42067), and enable Masquerade / NAT to have internet on the tunnel. Click ''Apply''. |
| ====Note for Access Point mode==== | ====Note for Access Point mode==== | ||
| Line 57: | Line 57: | ||
| ====Android/iOS config import==== | ====Android/iOS config import==== | ||
| - | Android: [https://play.google.com/store/apps/details?id=com.wireguard.android Google Play Store], iOS: [https://itunes.apple.com/us/app/wireguard/id1441195209 Apple Store (12.0 or later)] | + | Android: [https://play.google.com/store/apps/details?id=com.wireguard.android Google Play Store], iOS: [https://itunes.apple.com/us/app/wireguard/id1441195209 Apple Store (12.0 or later)]<br> |
| - | WireGuard app: press "+" in the lower right corner, select "Create from QR code", | + | WireGuard app: press "+" in the lower right corner, select "Create from QR code", scan from DD-WRT peer, then the app will prompt to name the tunnel. Public IP can be checked [http://whatismyip.akamai.com/advanced here]. |
| - | + | ||
| ====Linux config import==== | ====Linux config import==== | ||
Revision as of 23:37, 21 January 2020
VPN -> Wireguard
Contents |
WireGuard® is an extremely simple yet fast and modern VPN that utilizes state-of-the-art cryptography. It aims to be faster, simpler, leaner, and more useful than IPsec, while avoiding the massive headache. It intends to be considerably more performant than OpenVPN.
Some key points about Wireguard:
- Layer 3 only - no bridging
- UDP only
- SSH authenticated keys
- Executes within the Linux kernel
- Static routing
How it works
Quick Start
Conceptual Overview
Why WireGuard + DD-WRT tunnel?
This tutorial shows the basics of securely creating a tunnel from a client device to DD-WRT. Before proceeding, verify a working reset button and configuration backup in case of problems.
What is a QR Code?
The "Quick Response" Code is a two-dimensional barcode with larger encoded data capacity and high fault tolerance. Since build 38581 in February 2019, a client config can be imported using a QR Code. The advantage of this approach is that there is no need to transfer sensitive information via potentially compromised data channels.
Setup Instructions
The Wireguard installation/downloads page has software and instructions per OS.
- For the latest updated information and additional scripts see the Wireguard setup guide:
- Setup DDWRT router as a Wireguard server
- Client devices setup
- Setup DDWRT router as a Wireguard client
- Policy Based Routing for Wireguard
- Wireguard PBR Kill Script
- Info regarding changes for CVE-2019-14899 (ticket 6928)
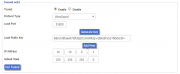
Create the Wireguard tunnel:
DD-WRT Basic -> Tunnels tab: enable the Tunnel then select WireGuard for Protocol Type.
- Generate Key and enter the oet1 interface IP: must be a network outside the local LAN range
- E.g. if the router LAN IP is 192.168.2.1, for the oet1 IP address use 10.10.0.1.
Add Peers:
For simple configurations, just enter Peer Tunnel IP within the oet1 interface ip range (e.g. 10.10.0.2) and Peer Tunnel DNS (8.8.8.8). Peer Tunnel MTU will be calculated automatically (WAN mtu-40) but can then be edited. Click Save then the QR-Code button to generate it.
Masquerade the tunnel:
Wireguard must be unbridged, using Forwarding and NAT. Go to Networking, unbridge the oet1 interface (automatic since r42067), and enable Masquerade / NAT to have internet on the tunnel. Click Apply.
Note for Access Point mode
Add the following firewall rule under Administration/Commands and save as firewall then reboot:
iptables -t nat -I POSTROUTING -o br0 -j SNAT --to $(nvram get lan_ipaddr)
Android/iOS config import
Android: Google Play Store, iOS: Apple Store (12.0 or later)
WireGuard app: press "+" in the lower right corner, select "Create from QR code", scan from DD-WRT peer, then the app will prompt to name the tunnel. Public IP can be checked here.
Linux config import
systemd-networkd 237, networkmanager 1.16, and connman (git since 18 Jan 2020) support Wireguard and preshared key.
Review the Wireguard install page, Linux distribution wiki (e.g. for Arch) and/or forums for more specific details.
- Go to Tunnels to generate then capture and save a QR Code screenshot
- Open the QR Code decoder and add the png file to decode
- You will be prompted with a decoded textual config file
- Use it to populate wireguard client config in the network manager
Windows config import
Windows Wireguard client: Windows .msi installer
Graphical QRCode decoder e.g. CodeTwo QR Code Reader
Options
Persistent Keep Alive: This is seconds between keep alive messages, and is optional. Default is 0 (Disabled). The recommended value for NAT'd devices is 25 seconds.
Allowed IPs: This is required and represents IP addresses that this peer is allowed to use inside the tunnel. Usually the peer's tunnel IP addresses and the networks the peer routes through tunnel. Outgoing packets will be sent to the peer whose Allowed IPs contain the destination address, and for multiple matches, the longest matching prefix is chosen. Incoming packets are only accepted if traffic to their source IP would be sent to the same peer. May be specified multiple times.
Preshared Key: A base64 preshared key generated by wg genpsk. This is optional and may be omitted. This adds an additional layer of symmetric-key cryptography into the existing public-key cryptography, for post-quantum resistance.
Troubleshooting
If you find any bugs report to: team@wireguard.com
- Start with rebooting all Peers
- Enable syslogd at Services/Services/Sytem Log
- In the script enable DEBUG by uncommenting the line:
#DEBUG= # uncomment/comment to enable/disable debug mode
Useful console commands
Check the tunnel status:
# wg interface: oet1 public key: blablaPyAN3eOyINB5JKNu4mHyKwrg3Mblabla= private key: (hidden) listening port: 51820 peer: BLABLAT3TQJwIE0OYx2qeZWYystRb9BLABLAbla= endpoint: 212.200.181.116:9208 allowed ips: 0.0.0.0/0 latest handshake: 7 seconds ago transfer: 14.11 KiB received, 39.85 KiB sent
Check if the oet1 network is NAT'd:
# iptables -t nat -v -n -L Chain POSTROUTING (policy ACCEPT 75 packets, 5466 bytes) pkts bytes target prot opt in out source destination 71 14687 SNAT 0 -- * ppp0 192.168.2.0/24 0.0.0.0/0 to:your_router_public_ip 38 2381 SNAT 0 -- * ppp0 10.0.0.0/24 0.0.0.0/0 to:your_router_public_ip
wg showconf oet1
ip addr
ip route show
- More: ifconfig, traceroute, and ping
Dynamic WAN IP on router
After importing configs from DD-WRT to Android/iOS app, edit the Endpoint in the Peer section e.g.:
- my.ddns.address.com:51820
Adding a second peer breaks the first
Allowed IPs of 0.0.0.0/0 cannot be used for both peers as it causes a collision. Instead set separate peer IPs e.g. 10.10.0.2/32 and 10.10.0.3/32. The Allowed IP's feature is for crypto routing. The key is valid for the entire allowed IP space.
Resolving local hostnames in the tunnel
DD-WRT GUI Services -> DNSMasq section: enable "Local DNS" and disable "No DNS Rebind", go to Tunnels to enter local DNS IP (e.g. 192.168.1.1) for Peer Tunnel DNS (repeat for every peer). Since Wireguard cannot be bridged, the wireguard interface or it's local IP needs specified in dnsmasq as an additional binding interface / listener (interface=oet1). There is also an nvram parameter "dnsmasq_addif" to specify custom additional interfaces (nvram set dnsmasq_addif=oet1).
- The easiest way is to simply add a DHCP interface at Setup -> Networking since the client is not requesting any IP, nothing special will happen. DHCP is present and reachable, but unused.
Reference
DD-WRT source: Wireguard changesets
DD-WRT forum: Wireguard
Wireguard Git Repository
WireGuard Mailing Lists
Wireguard DD-WRT setup (by wuruxu on Github)