Station Mode
From DD-WRT Wiki
| Revision as of 14:44, 9 July 2006 (edit) 219.240.12.173 (Talk) (→Introduction) ← Previous diff |
Current revision (20:21, 19 December 2023) (edit) (undo) Kernel-panic69 (Talk | contribs) |
||
| (100 intermediate revisions not shown.) | |||
| Line 1: | Line 1: | ||
| - | + | '''''Wiki Path''''': [[Main_Page|DD-WRT Wiki Main]] / [[Tutorials]] / [[Linking Routers]] / '''Client Mode''' | |
| + | ---- | ||
| + | [[image:Client_Bridge.jpg|660px]]<br> | ||
| + | The secondary (station) router is unbridged in a different subnet (with NAT), while a [[Client_Bridge|Station Bridge]] or [[Client_Bridged|Station Bridge (Routed)]] is the same subnet as the host. | ||
| - | =Introduction= | + | ==Introduction== |
| - | This | + | This mode is NOT for WIRED connections between two routers, like an Access Point. It is a wireless connection between two routers only, usually to the primary gateway router. A Station Mode router connects to a Wireless Access Point (WAP) wireless connection as the WAN interface, and shares the internet connection only to the LAN ports, or a separate WAP for multi-radio routers. It is not seen as a WAP, nor accepts wireless connections by other client devices. |
| - | + | The primary (host) router is not required to be running DD-WRT firmware. The primary and secondary (Station Mode) routers must be on separate subnets, and NAT is used between them. Thus, when port forwarding is needed it must be configured at both routers - not just on the host router. | |
| + | |||
| + | A Station Mode router uses its own DHCP server for IP Address, Gateway, and DNS server to connected devices. To have computers connected to both routers (main and secondary) and co-exist in the same subnet, set up DD-WRT as a [[Client_Bridge|Station Bridge]](Broadcom), [[Client_Bridged|Station Bridge (Routed)]], [[Repeater Bridge]], or use [[WDS_Linked_router_network|WDS]]. Further explanation of bridging modes is at [[Linking_Routers|Linking Routers]]. | ||
| - | + | *'''<font color=darkred>If using a multi-band router, do not set more than one band to CB.</font>''' The other radio(s) would normally be set as ''AP''. For example, the 2.4GHz radio can a CB while the 5GHz is an AP, or vice versa. | |
| - | + | ||
| - | + | ||
| - | = | + | ==Station Mode Setup== |
| - | + | The secondary station router will be on a different subnet than the primary host router. For example, if the host router IP address is 192.168.1.1, configure the station router to 192.168.2.1. | |
| + | #These instructions assume a reset router. '''Broadcom routers:''' read the [http://www.dd-wrt.com/phpBB2/viewtopic.php?t=51486 Peacock thread] | ||
| + | #Connect a cable from your computer to the LAN port on your router. | ||
| + | #''(Optional)'' Set your computer to a static IP address (e.g. 192.168.1.7, subnet 255.255.255.0) | ||
| + | #Connect to the DD-WRT GUI at 192.168.1.1 in a browser | ||
| + | #Set a username and password - if not asked for this, do a proper [[Reset_And_Reboot|reset]]! | ||
| + | #Go to ''Wireless'': '''these settings must match the primary host router - '''Check spelling and case!''' | ||
| + | #*In ''Wireless->Basic Settings'' and change the ''Wireless Mode'' to "Station" | ||
| + | #*Set the ''Wireless Network Name (SSID)'' to exactly match the primary router. Click ''Save'' ('''not''' ''Apply'') | ||
| + | #**If multiple routers broadcast the same SSID, to connect to a specific one (i.e. the primary router, instead of a repeater), enable MAC Filtering on the Wireless Tab, and add the specific device's MAC Address. | ||
| + | #**MAC Address can be found on the "Site Survey" page, linked from the ''Wireless'' tab in ''Status'' | ||
| + | #*''Wireless Security'': set the ''Security Mode'' and other information same as primary router. Click ''Save'' ('''not''' ''Apply'') | ||
| + | #''(Optional)'' If available, in ''Wireless'' tab (or under ''Advanced''), set (or disable) the Ack Timing in meters | ||
| + | #Go to ''Setup->Basic Setup'': if needed, change ''Connection Type'' to ''Static IP'' from "Automatic Configuration - DHCP" | ||
| + | #*Static IP allows easier access remote GUI, SSH, or telnet access is enabled under ''Administration'' | ||
| + | #*If the station router requires external management, go to ''Setup->Basic Setup'', set the WAN port protocol as needed and enter info provided by your ISP. This is the setting that is bonded to the wireless interface. | ||
| + | #In ''Network Setup'' set the Local IP Address '''to a different subnet''' from the primary host router (e.g. 192.168.2.1) | ||
| + | #Set the ''Gateway'' address to the '''primary host router gateway''' or internet will not work (e.g. 192.168.1.1) | ||
| + | #*The device should be in GATEWAY ''Advanced Routing'' mode, not ROUTER, or Masquerade/NAT does not happen. | ||
| + | #''(Optional)'' Set your local DNS to the IP address of your station router | ||
| + | #''(Optional)'' Set Static DNS servers in ''Network Address Server Settings (DHCP)'' if not provided or wanted from WAN | ||
| + | #''(Recommended)'' Change the Time Zone and DST settings as needed. | ||
| + | #''(Optional)'' Set a "Server IP/Name" in ''Time Setting'' section for NTP (blank uses a default server) | ||
| + | #Click ''Save'' ('''not''' ''Apply'') | ||
| + | #''(Optional)'' In ''Security->Firewall'', disable ''SPI Firewall'' '''if security between AP & Station is not needed''' | ||
| + | #Click ''Apply'', then change the computer back to auto IP/DNS if needed (replug the LAN cable if not working) | ||
| + | #Let the station router reboot and connect to the host, then configure '''on the new Station IP address''' as needed | ||
| + | #If not working, unplug the router for 30sec and retry | ||
| - | + | ==Station Mode Restrictions== | |
| + | To allow internet access but prevent ''192.168.1.x'' clients from seeing each other on ''br0'', use this firewall script (iptables): | ||
| + | iptables -I FORWARD -i br0 -d 192.168.1.0/24 -j DROP | ||
| - | + | ==Troubleshooting== | |
| + | If the preceding instructions do not work, it is usually an encryption or password problem. Disable encryption on the primary router and retry the setup. Using proper encryption and the correct case-sensitive password is key. Do a reset and start over. Note: WPA2-AES (aka CCMP) ''is required for 802.11N (and newer) devices''. | ||
| - | Für diese, die alle Rechner im selben Subnetz wollen, man kann den WRT im [[Wireless Bridge]] Mode laufen lassen. | ||
| - | + | [[Category:Wlan]][[Category:Linking Routers]] | |
| - | + | ||
| - | + | ||
| - | + | ||
| - | + | ||
| - | + | ||
| - | + | ||
| - | + | ||
| - | + | ||
| - | + | ||
| - | + | ||
| - | + | ||
| - | + | ||
| - | + | ||
| - | + | ||
| - | + | ||
| - | + | ||
| - | + | ||
| - | + | ||
| - | + | ||
| - | + | ||
| - | + | ||
| - | + | ||
| - | + | ||
| - | + | ||
| - | + | ||
| - | [[Category: | + | |
| - | + | ||
| - | [[Category: | + | |
Current revision
Wiki Path: DD-WRT Wiki Main / Tutorials / Linking Routers / Client Mode
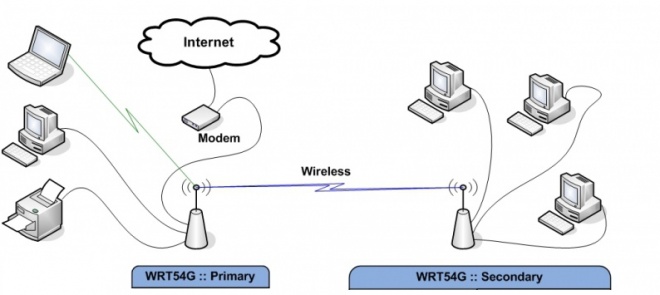
The secondary (station) router is unbridged in a different subnet (with NAT), while a Station Bridge or Station Bridge (Routed) is the same subnet as the host.
Contents |
[edit] Introduction
This mode is NOT for WIRED connections between two routers, like an Access Point. It is a wireless connection between two routers only, usually to the primary gateway router. A Station Mode router connects to a Wireless Access Point (WAP) wireless connection as the WAN interface, and shares the internet connection only to the LAN ports, or a separate WAP for multi-radio routers. It is not seen as a WAP, nor accepts wireless connections by other client devices.
The primary (host) router is not required to be running DD-WRT firmware. The primary and secondary (Station Mode) routers must be on separate subnets, and NAT is used between them. Thus, when port forwarding is needed it must be configured at both routers - not just on the host router.
A Station Mode router uses its own DHCP server for IP Address, Gateway, and DNS server to connected devices. To have computers connected to both routers (main and secondary) and co-exist in the same subnet, set up DD-WRT as a Station Bridge(Broadcom), Station Bridge (Routed), Repeater Bridge, or use WDS. Further explanation of bridging modes is at Linking Routers.
- If using a multi-band router, do not set more than one band to CB. The other radio(s) would normally be set as AP. For example, the 2.4GHz radio can a CB while the 5GHz is an AP, or vice versa.
[edit] Station Mode Setup
The secondary station router will be on a different subnet than the primary host router. For example, if the host router IP address is 192.168.1.1, configure the station router to 192.168.2.1.
- These instructions assume a reset router. Broadcom routers: read the Peacock thread
- Connect a cable from your computer to the LAN port on your router.
- (Optional) Set your computer to a static IP address (e.g. 192.168.1.7, subnet 255.255.255.0)
- Connect to the DD-WRT GUI at 192.168.1.1 in a browser
- Set a username and password - if not asked for this, do a proper reset!
- Go to Wireless: these settings must match the primary host router - Check spelling and case!
- In Wireless->Basic Settings and change the Wireless Mode to "Station"
- Set the Wireless Network Name (SSID) to exactly match the primary router. Click Save (not Apply)
- If multiple routers broadcast the same SSID, to connect to a specific one (i.e. the primary router, instead of a repeater), enable MAC Filtering on the Wireless Tab, and add the specific device's MAC Address.
- MAC Address can be found on the "Site Survey" page, linked from the Wireless tab in Status
- Wireless Security: set the Security Mode and other information same as primary router. Click Save (not Apply)
- (Optional) If available, in Wireless tab (or under Advanced), set (or disable) the Ack Timing in meters
- Go to Setup->Basic Setup: if needed, change Connection Type to Static IP from "Automatic Configuration - DHCP"
- Static IP allows easier access remote GUI, SSH, or telnet access is enabled under Administration
- If the station router requires external management, go to Setup->Basic Setup, set the WAN port protocol as needed and enter info provided by your ISP. This is the setting that is bonded to the wireless interface.
- In Network Setup set the Local IP Address to a different subnet from the primary host router (e.g. 192.168.2.1)
- Set the Gateway address to the primary host router gateway or internet will not work (e.g. 192.168.1.1)
- The device should be in GATEWAY Advanced Routing mode, not ROUTER, or Masquerade/NAT does not happen.
- (Optional) Set your local DNS to the IP address of your station router
- (Optional) Set Static DNS servers in Network Address Server Settings (DHCP) if not provided or wanted from WAN
- (Recommended) Change the Time Zone and DST settings as needed.
- (Optional) Set a "Server IP/Name" in Time Setting section for NTP (blank uses a default server)
- Click Save (not Apply)
- (Optional) In Security->Firewall, disable SPI Firewall if security between AP & Station is not needed
- Click Apply, then change the computer back to auto IP/DNS if needed (replug the LAN cable if not working)
- Let the station router reboot and connect to the host, then configure on the new Station IP address as needed
- If not working, unplug the router for 30sec and retry
[edit] Station Mode Restrictions
To allow internet access but prevent 192.168.1.x clients from seeing each other on br0, use this firewall script (iptables):
iptables -I FORWARD -i br0 -d 192.168.1.0/24 -j DROP
[edit] Troubleshooting
If the preceding instructions do not work, it is usually an encryption or password problem. Disable encryption on the primary router and retry the setup. Using proper encryption and the correct case-sensitive password is key. Do a reset and start over. Note: WPA2-AES (aka CCMP) is required for 802.11N (and newer) devices.