Internal device network
From DD-WRT Wiki
Your network device's (commonly wrongly known as a "router") has an internal network. The default internal device networks connects the physical(=hardware):
- internal switch
- wireless access point
with the network processor (ARM, mips...).
In the network processor, via the DD-WRT user interface (or the manufacturers firmware), the you can define, limited by software implementation and hardware possibilities, how the hardware is logically interconnected to user created software network services.
List of possible software network services:
- OSI layer 2 interconnection - ethernet address routing; bridge (ca.= software switch)
- OSI layer 3 interconnection - ip address routing; a software router
- OSI layer 2-7 moderation, ethernet transparent/bridging firewall, OSI layer 2-7 firewall
- OSI layer 3-7 moderation; common ip firewall, OSI layer 3-7 firewall
The software network services is connected by you, to physical or logical network interface. The interfaces might be a:
- physical interfaces might be labelled eth0, eth1...
- logical might be a bridge (=switch) labelled br0, br1...
- logical vlan labelled vlan0, vlan1....
and maybe:
- teql0 - load sharing device I believe this is used for the "Link Aggregation on Ports 3 & 4" option on the Setup/Vlans page.
- imq0,1 - QOS device or IMQ Device
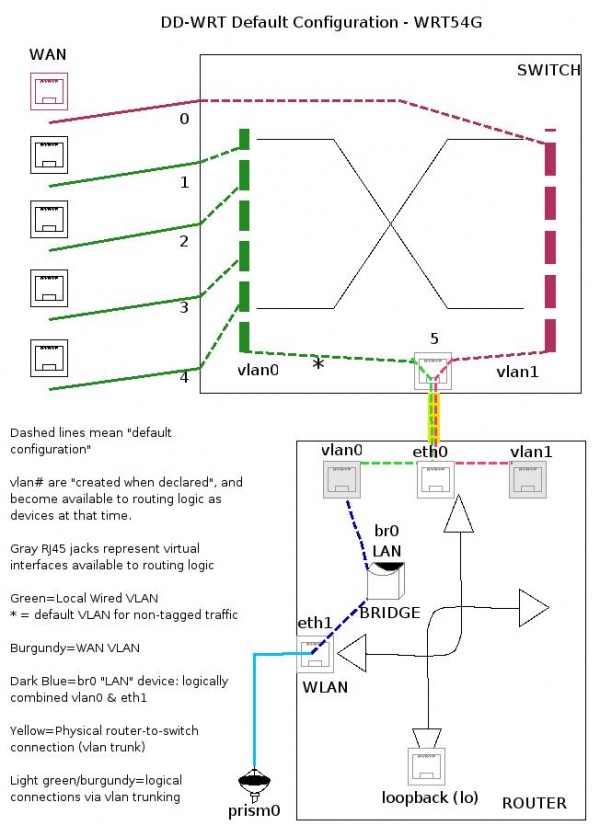
The default internal device networks in a non-802.11n network device - specifically the default configuration of a DD-WRT V23-SP2 firmware on a Linksys WRT54G v2. In a network device containing a 802.11n wireless access point the internal numbering of ports, bridges and vlans are different.